
3D printing and CNC milling solutions for producing custom foot orthotics in-office with professional CAD design software.
We provide comprehensive orthopedic solutions with industry-leading technology, expertise, and support.
Our CNC milling machines and 3D printers deliver unmatched precision for orthopedic applications.
Specialized software solutions for design, analysis, and patient management.
Comprehensive training, maintenance, and technical support from industry experts.
Explore our most popular orthopedic technology solutions.

Compact, precision CNC milling for orthotic and prosthetic applications.
Learn More →
High-resolution 3D printing system designed for orthopedic applications.
Learn More →
Custom orthotic modeling software with precision design tools and intuitive workflow.
Learn More →Our complete digital workflow transforms the way you create custom foot orthotics, from initial scan to finished product.
Capture precise 3D models of your patient's feet in seconds using our advanced scanning technology.
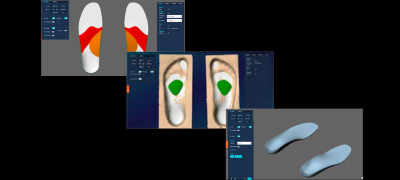
Use OrthoCAD software to create and modify orthotic designs with precision and digital efficiency.
Produce custom orthotics with either 3D printed orthotics technology or precision CNC orthotic milling.
Fit patients with custom orthotics in a single visit, eliminating weeks of waiting for laboratory production.
Modern orthotic CADCAM technology delivers significant advantages over traditional casting and outsourced manufacturing methods.
Create custom orthotics in hours instead of weeks with in-house production using 3D printed orthotics or CNC orthotic milling.
Digital scanning captures 1000× more data points than foam impressions or plaster casts, resulting in superior fit.
Reduce costs while increasing margins by eliminating outsourcing fees and shipping expenses.
Impress patients with modern technology and same-day delivery of custom orthotic solutions.

In-office orthotic CADCAM production eliminates weeks of lab time.
With the Apex Belt V2, 3D printed orthotics can be produced in-house with minimal supervision and maximum efficiency.
Common questions about orthotic CADCAM, 3D printed orthotics, and CNC orthotic milling
3D printed orthotics are created through an additive process, building the orthotic layer by layer using specialized materials. This allows for complex geometries and variable densities. CNC orthotic milling uses a subtractive process, carving the orthotic from a solid block of material, which can work with traditional materials like EVA and is often faster for certain designs. Both are valid approaches to modern orthotic production with different advantages.
Most practices can implement orthotic CADCAM systems with just 1-2 days of training. Our comprehensive training program covers 3D scanning, design software, and manufacturing equipment operation. The software is intuitive, and both 3D printing and CNC milling processes are largely automated. Most clients are creating custom orthotics independently within the first week of implementation.
Most practices see a return on investment within 6-18 months depending on volume. Producing orthotics in-house eliminates lab fees of $50-150 per pair, while material costs for 3D printed orthotics or CNC milled orthotics range from $10-30 per pair. Additionally, offering same-day service often allows practices to command premium pricing and attract more patients, further accelerating ROI.
Yes, both 3D printed orthotics and CNC milled orthotics match or exceed the durability of traditionally manufactured orthotics. 3D printed orthotics use advanced materials specifically engineered for orthotic applications with excellent durability and flexibility. CNC orthotic milling can use the same traditional materials as lab-produced orthotics but with greater precision and consistency.
Yes, we offer multiple financing options to make adopting orthotic CADCAM technology more accessible. This includes equipment leasing, 0% promotional financing, and graduated payment plans that align with your increasing production capacity. Many practices find that monthly financing payments are offset by savings from in-house production within the first few months.
Still have questions about 3D printed orthotics or CNC orthotic production?
Contact Our TeamContact our team today to discuss how VertexOrthopedic solutions can benefit your practice or research facility.